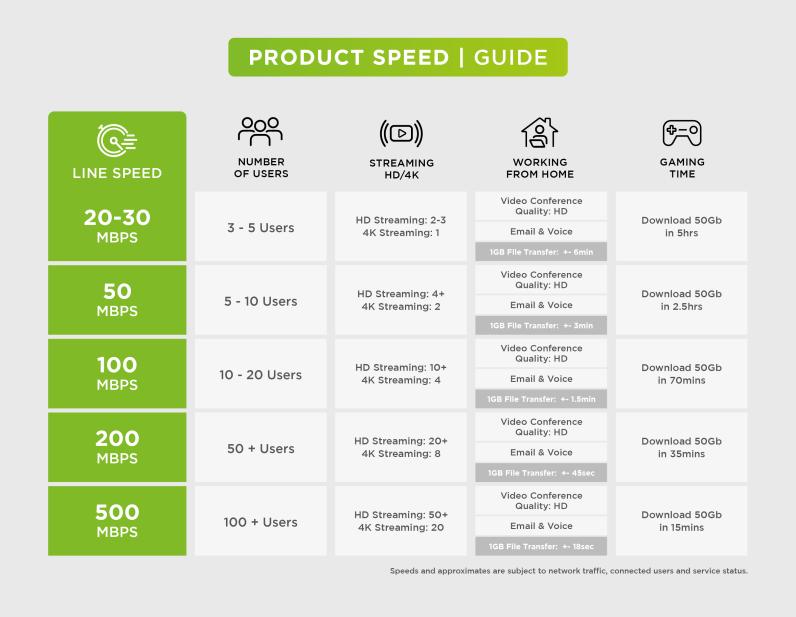
Wireless technology can be quite confusing, so let’s break down the differences between Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6, and the latest Wi-Fi 7, as well as the distinctions between the 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz frequency bands.
Frequency Bands
There are three main frequency bands used by wireless devices: 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz.
• 2.4GHz: This band offers a longer range and better penetration through walls and obstacles, making it suitable for larger areas. However, it is slower and more susceptible to interference from other devices like microwaves and Bluetooth gadgets.
• 5GHz: This band provides faster internet speeds and is less prone to interference, but it has a shorter range. It’s ideal for high-density wireless networks, such as in apartments or office buildings.
• 6GHz: The newest addition, 6GHz, offers even more bandwidth, reducing congestion and interference significantly. It supports multi-gigabit speeds and is designed for the latest Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7 devices.
Wi-Fi Standards
Now, let’s discuss the Wi-Fi standards:
• Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac):This is the previous generation of Wi-Fi, offering decent speeds and reliability. 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz
• Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax): The current standard, Wi-Fi 6, provides faster internet speeds, improved reliability, and better connectivity for multiple devices simultaneously. It’s designed to handle the increasing demand for internet connectivity and can support more devices on a single network. Expected real-life speeds at arounds 800-1200 Mbps
2.4 GHz & 5 GHz
• Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax): The current standard, Wi-Fi 6, provides faster internet speeds, improved reliability, with Extended spectrum that includes 6Ghz, to reduced interference. 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, & 6 GHz
• Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be): The upcoming Wi-Fi 7 standard promises even greater improvements, including significantly higher speeds, lower latency, and enhanced capacity to support more devices. It aims to further optimize performance in dense environments and provide a seamless experience for emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). Expected real-life speeds at arounds 2-5 Gbps
2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, & 6 GHz
Compatibility
To take full advantage of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7, you need compatible devices. While Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 routers are backwards compatible and can connect to older devices, those devices will still operate on the older Wi-Fi standards and won’t benefit from the enhanced speeds and connectivity.
Recommendations
We recommend upgrading to Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 7 if you require wireless speeds above 400Mbps or if you have multiple devices that need a stable and fast connection